Configure your network
Protecting your organization's public networks
To protect Internet-facing IP address spaces of your organization, you can configure network IP ranges using the network based deployment functionality. A network can contain a group of IPv4 addresses or blocks. Please ensure to add all your public facing IPs under the network section. Once a network has been registered on the DNS Firewall console, DNS traffic from the network needs to be forwarded to DNS Firewall's public resolvers Deploy Roaming clients.
Configure external networks
To add devices, which use your router to access the internet, to the DNS Firewall monitoring:
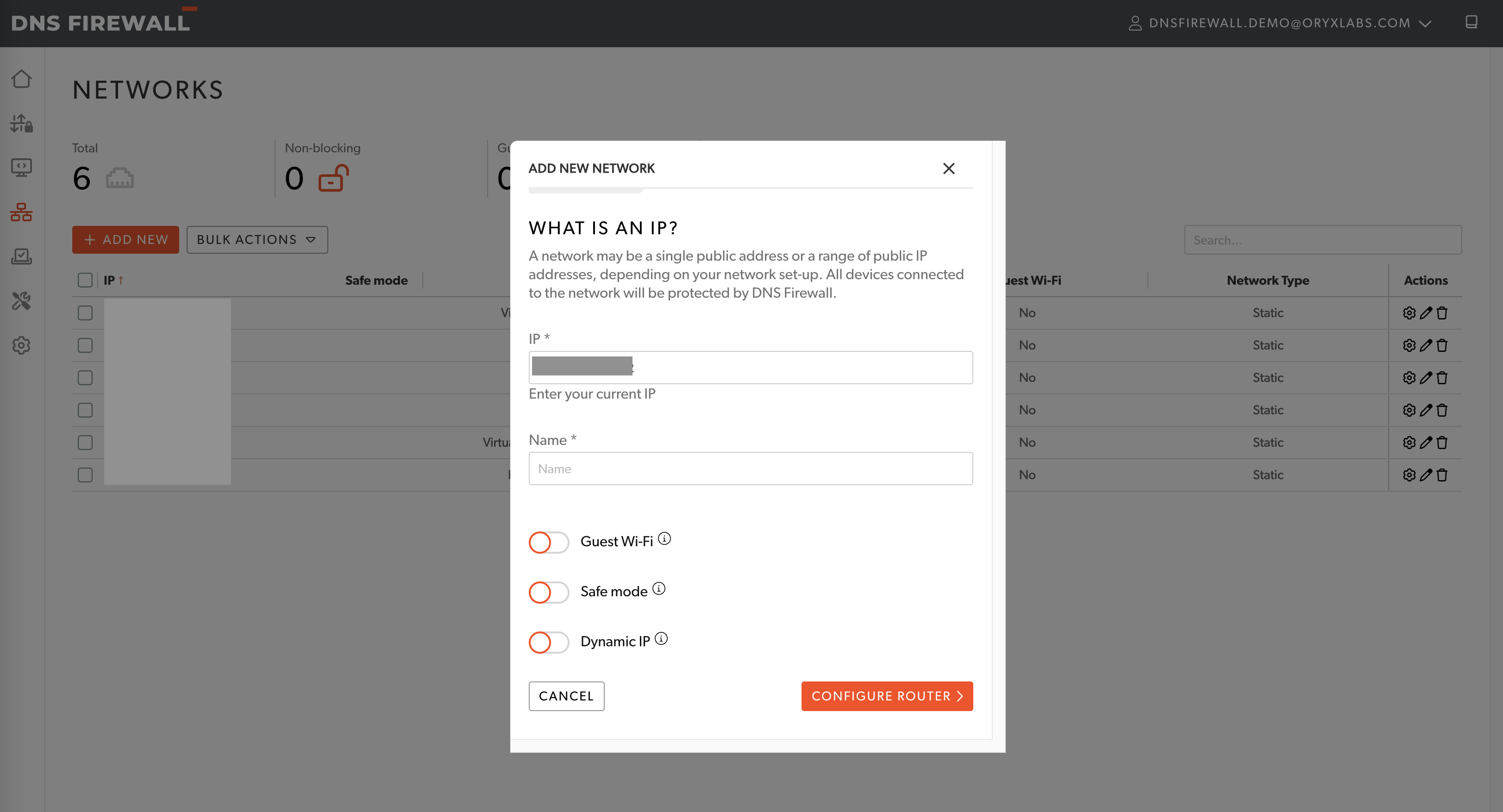
- From the web application, navigate to Networks > Add new
- Add the below details about the network:
- Enter a valid IPv4 address and netmask. This step can be skipped if the network has a dynamic IP.
- Add a unqiue name to identify the network.
- Select if the network is a guest wifi. This option will help prevent the block page from being shown on the guest wifi network.
- Select if the network will operate in safe mode. When safe mode is enabled, DNS Firewall will not enforce any rejection policy.
- Enable dynamic IP if the network used doesn't have a static IP linked to it. Refer to Configure Dynamic IP for more details.
- Click on 'Configure Router' to get specific details on the set-up.
- For details on DNS Firewall configuration on MS Active Directory, please refer AD configuration.
- For details on DNS Firewall configuration on Dnsmasq, please refer Dnsmasq configuration.
Manage existing networks
To manage an existing network, navigate to Networks. Click on 'Edit' icon for the network you want to update. All attributes of a network that were captured during network creation can be updated.
Verify if a network is properly configured
On a device connected to the configured network, visit a few domains through a browser of choice. After a few seconds, verify if the DNS requests appear under DNS Requests > All DNS Requests.
Please note, all requests from a network will have the same source IP as that of the network. In case you want to identify the individual device that made a specific DNS request, please refer to Network end user tracing