DNS
What is DNS?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the phonebook of the Internet. DNS translates the domain name that you type in the browser (such as www.example.com) to a computer-friendly IP address (93.184.216.34), similar to how a phonebook translates a person’s name to a phone number. The IP address identifies the exact server where the website data is stored, allowing the browser to contact the server and load the page.
What happens behind the scenes of a DNS lookup?
- The user types "example.com" into their web browser. The browser sends this query to a recursive DNS server.
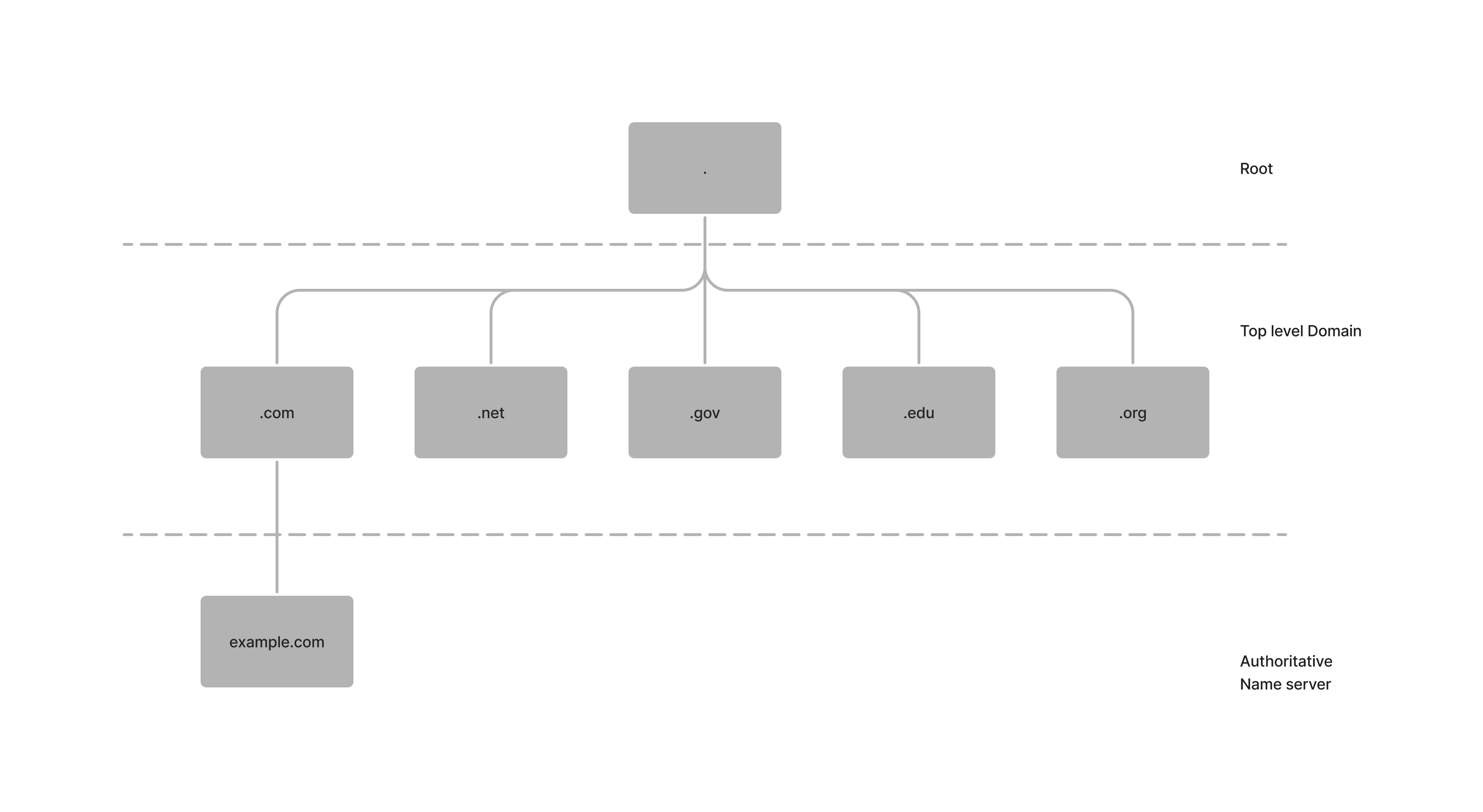
- The recursive DNS server starts its search at the root of the DNS hierarchy. The root servers are responsible for knowing where the top-level domains (TLDs) are located, such as .com, .net, and .org.
- The root server tells the recursive DNS server where the .com TLD server is located.
- The recursive DNS server then queries the .com TLD server for the address of the authoritative DNS server for example.com.
- The .com TLD server tells the recursive DNS server the address of the authoritative DNS server for example.com.
- The recursive DNS server then queries the authoritative DNS server for example.com for the IP address of the web server hosting example.com.
- The authoritative DNS server for example.com returns the IP address of the web server to the recursive DNS server.
- The recursive DNS server then returns the IP address of the web server to the browser.
- The browser uses the IP address to connect to the web server and load the example.com website.